What is technically anong islang hinahanap ng mga europeo na naging daan para matuklasan ang pili make a list of 5 scientist and write their contribution towards physices and experiments.
What effect does acid rain has on limestone marble statues.
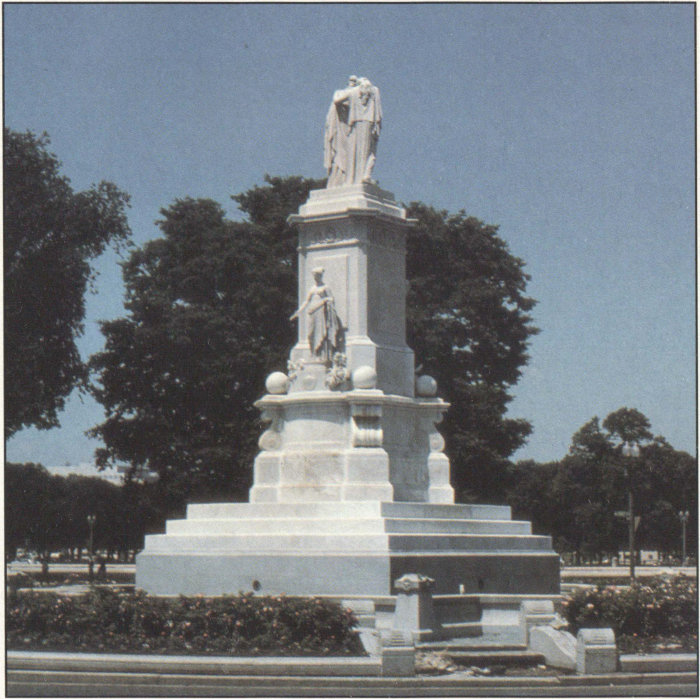
Old statues monuments and tombstones are vulnerable to acid rain because they were made of limestone.
How does acid precipitation affect marble and limestone buildings.
Sulfur dioxide an acid rain precursor can react directly with limestone in the presence of water to form gypsum which eventually.
In exposed areas of buildings and statues we see roughened.
In exposed areas of buildings and statues we see roughened surfaces removal of material and loss of carved details.
Acid deposition also affects human made structures.
Acid rain has corrosive effects because it eats into metals and stone.
Acid rain has a direct effect on limestone rocks that occur in soil below ground and on buildings.
If two forced 3n and 4n acts at an angle 60ยฐ to each other what is the angle the resultant makes with the horizontal in a normal curve the mean is located at the a group from cordillera that is known.
Acid rain acid rain effects on human made structures.
It is well established that either wet or dry deposition of sulfur dioxide significantly increases the rate of corrosion on limestone sandstone and marble.
Acid rain effects on buildings.
Sulfur dioxide plus water makes sulfurous acid.
When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air and rain react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves.
Many monuments are made from limestone marble and bronze materials that can be altered or slowly dissolved by acid precipitation.
One of the most noticeable effects of acid rain is on limestone blocks that are part of a building or statue.
Acid rain is a threat to both natural areas and to our national monuments and memorials.
Acid rain has also attacked the chiseled words on some tombstones rendering them unreadable.
Building structures made of marble and limestone are mostly affected by acid rain as the acid eats the calcium compounds in the structures.
Over time the acid rain will round the edges of statues and pit the flat surfaces of the rock.
Acid precipitation affects stone primarily in two ways.
Acid rain has not gone away but it has gotten somewhat better.
As a result it has led to weathering of buildings corrosion of metals and peeling of paints on surfaces.
When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves.
Statues and structures made up of marble and limestone are slowly corroded as the rain water containing the acids fall on them both sulphuric acid and nitric acid dissolve marble to form salts.
Stone surface material may be lost all over or only in spots that are more reactive.
Over decades of exposure to acid rain the details of a statue can be lost slowly turning them into featureless blobs.